SpringBoot的web开发能力,由SpringMVC提供。
WebMvcAutoConfiguration原理 生效条件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @AutoConfiguration(after = { DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class }) @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class }) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class) @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10) @ImportRuntimeHints(WebResourcesRuntimeHints.class) public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration
效果
放了两个Filter
HiddenHttpMethodFilter:页面表单提交rest请求(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE)FormContentFilter:表单内容Filter,(servlet规范中,只有get、post请求,这个filter就是为了处理put和delete请求)GET(数据放url后面)、POST(数据放请求体)请求可以携带数据,PUT、DELETE的请求体数据会被忽略
给容器中放了一个WebMvcConfigurer组件,给SpringMVC添加各种定制功能
所有的功能最终会和配置文件进行绑定
WebMvcProperties:spring.mvc配置文件WebProperties:spring.web配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class) @EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, WebProperties.class }) @Order(0) public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer , ServletContextAware
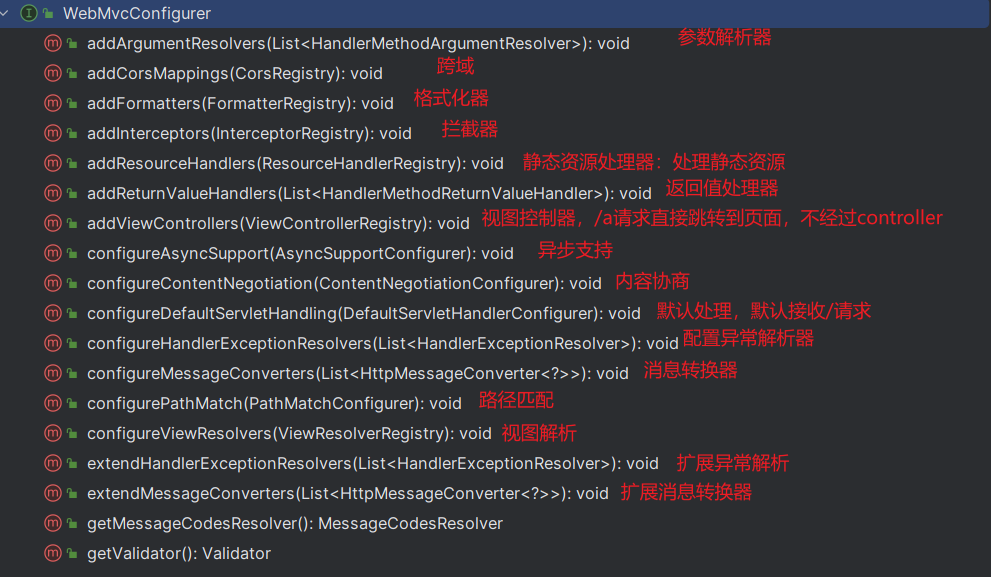
提供了配置SpringMVC底层的所有组件入口
静态资源规则源码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Override public void addResourceHandlers (ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) if (!this .resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) { logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled" ); return ; } addResourceHandler(registry, this .mvcProperties.getWebjarsPathPattern(), "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/" ); addResourceHandler(registry, this .mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> { registration.addResourceLocations(this .resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()); if (this .servletContext != null ) { ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this .servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION); registration.addResourceLocations(resource); } }); }
规则一:访问/webjars/**路径就去classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/下找资源
规则二:访问/**路径就去静态资源默认的四个位置找资源
classpath:/META-INF/resources/
classpath:/resources/
classpath:/static/
classpath:/public/
规则三:静态资源,默认都有缓存规则的设置
所有缓存的设置,都可以通过配置文件修改spring.web
cachePeriod:缓存周期,多久不用找服务器要新的,默认没有,以s为单位cacheControl:HTTP缓存控制;HTTP 缓存 - HTTP | MDN useLastModified:是否使用最后一次修改(判断最后修改时间,如果未修改使用缓存),配合HTTP Cache规则
如果浏览器访问了一个静态资源index.js,如果服务器上这个资源没有发生变化,下次访问的时候就可以直接让浏览器用自己缓存中的东西,而不用给服务器发请求。
1 2 3 registration.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(this .resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod())); registration.setCacheControl(this .resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl()); registration.setUseLastModified(this .resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified());
EnableWebMvcConfiguration源码 1 2 3 4 5 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @EnableConfigurationProperties(WebProperties.class) public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration implements ResourceLoaderAware
在这个配置类里面,会放一个组件WelcomePageHandlerMapping(欢迎页)
HandlerMapping:根据请求路径寻找那个handler能处理请求
WelcomePageHandlerMapping:
访问/**路径下的所有请求,都在以前四个静态资源路径下找,欢迎页也一样
找index.html:只要静态资源的位置由一个index.html页面,项目启动默认访问
静态资源路径下找不到,会去根路径下找,如果还是找不到,会尝试从容器中找名称为index的视图
WebMvcConfigurer 是一个自动配置类,它里面有一个EnableWebMvcConfigurationEnableWebMvcConfiguration继承了DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration,这两个都生效DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration里面有一个WebMvcConfigurerComposite属性,该属性的setter方法会注入一个List<WebMvcConfigurer>类型的变量,spring会自动在容器中寻找所有的WebMvcConfigurer类型的Bean别人调用DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration的方法配置底层规则,而它调用所有WebMvcConfigurer的配置方法。
WebMvcConfigurationSupport提供了很多的默认设置。HttpMessageConverter
1 2 3 4 jackson2Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper" , classLoader) && ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerator" , classLoader); jackson2XmlPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.xml.XmlMapper" , classLoader); jackson2SmilePresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.smile.SmileFactory" , classLoader);
Web场景 自动配置 1、整合web场景
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency >
2、引入了autoconfigure自动配置功能@EnableAutoConfiguration注解使用@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)批量导入组件META-INF\spring\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports文件中配置的所有组件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestClientAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration ===========以下是响应式web场景和现在没有关系========== org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveMultipartAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebSessionIdResolverAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration =========以上是响应式web场景========== org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
6、绑定了配置文件的一堆配置项
SpringMvc的所有配置spring.mvc
Web场景通用配置spring.web
文件上传配置spring.servlet.multipart
服务器的配置server:比如:编码方式
默认效果 默认配置:
包含了 ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 和 BeanNameViewResolver 组件,方便视图解析
默认的静态资源处理机制 : 静态资源放在 static 文件夹下即可直接访问自动注册 了 Converter,GenericConverter,Formatter组件,适配常见数据类型转换 和格式化需求 支持 HttpMessageConverters,可以方便返回 json等数据类型 注册 MessageCodesResolver,方便国际化 及错误消息处理支持 静态 index.html自动使用 ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer,实现消息处理、数据绑定、类型转化、数据校验等功能
重要:
如果想保持 boot mvc 的默认配置 ,并且自定义更多的 mvc 配置,如:interceptors , formatters , view controllers 等。可以使用@Configuration 注解添加一个WebMvcConfigurer 类型的配置类,并不要标注 @EnableWebMvc
如果想保持 boot mvc 的默认配置,但要自定义核心组件实例,比如:RequestMappingHandlerMapping ,RequestMappingHandlerAdapter , 或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver ,给容器中放一个 WebMvcRegistrations 组件即可
如果想全面接管 Spring MVC,@Configuration 标注一个配置类,并加上 @EnableWebMvc 注解,实现 WebMvcConfigurer 接口
静态资源 默认规则 静态资源映射 静态资源映射规则在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中进行了定义:
/webjars/** 的所有路径 资源都在 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars//** 的所有路径 资源都在 classpath:/META-INF/resources/、classpath:/resources/、classpath:/static/、classpath:/public/所有静态资源都定义了缓存规则 。【浏览器访问过一次,就会缓存一段时间】,但此功能参数无默认值
period: 缓存间隔。 默认 0S;cacheControl:缓存控制。 默认无;useLastModified:是否使用lastModified头。 默认 false;
静态资源缓存
所有静态资源都定义了缓存规则 。【浏览器访问过一次,就会缓存一段时间】,但此功能参数无默认值
period: 缓存间隔。 默认 0S;cacheControl:缓存控制。 默认无;useLastModified:是否使用lastModified头。 默认 false;
欢迎页 欢迎页规则在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中进行了定义:
在静态资源目录下找index.html
没有就在templates下找index模板页
Facicon
在静态资源目录下找favicon.ico(是浏览器发起的)
缓存实验 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 server.port =9000 spring.web.resources.add-mappings =true spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.max-age =7200 spring.web.resources.cache.use-last-modified =true
自定义静态资源规则
自定义静态资源路径、自定义缓存规则
配置方式 spring.mvc:静态资源访问前缀路径spring.web:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 spring.web.resources.add-mappings =true spring.web.resources.cache.period =3600 spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.max-age =7200 spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.cache-public =true spring.web.resources.cache.use-last-modified =true spring.web.resources.static-locations =classpath:/a/,classpath:/b/,classpath:/static/ spring.mvc.webjars-path-pattern =/wj/** spring.mvc.static-path-pattern =/static/**
代码方式
容器中只要有一个WebMvcConfigurer组件,配置的底层行为都会生效
@EnableWebMvc //禁用boot的默认配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Configuration public class MyConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer @Override public void addResourceHandlers (ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**" ) .addResourceLocations("classpath:/a/" ,"classpath:/b/" ) .setCacheControl(CacheControl.maxAge(1180 , TimeUnit.SECONDS)); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Configuration public class MyConfig /*implements WebMvcConfigurer */ @Bean public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer () return new WebMvcConfigurer() { @Override public void addResourceHandlers (ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**" ) .addResourceLocations("classpath:/a/" , "classpath:/b/" ) .setCacheControl(CacheControl.maxAge(1180 , TimeUnit.SECONDS)); } }; } }
路径匹配
Spring5.3之后加入了更多的请求路径匹配 的实现策略;AntPathMatcher 策略,现在提供了PathPatternParser 策略,并且可以让我们指定到底使用哪种策略,默认PathPatternParser
Ant风格路径用法 Ant风格的路径模式语法具有一些规则:
*:表示任意数量的字符?:表示任意一个字符**:表示任意数量的目录{}:表示一个命名的模式占位符[]:表示字符集合,例如[a-z]表示所有小写字母
例如:
*.html 匹配任意名称,扩展名为.html的文件/folder1/*/*.java 匹配在folder1目录下的任意两级目录下的.java文件/folder2/**/*.jsp 匹配在folder2目录下任意目录深度的.jsp文件/{typr}/{id}.html 匹配任意文件名为{id}.html,在任意命名的{type}目录下的文件
注意:Ant风格的路径模式语法中的特殊字符需要转移,如:
要匹配文件路径中的星号,需要转义为\\*
要匹配文件路径中的文化,需要转义为\\?
模式切换
AntPathMatcher 与 PathPatternParser
PathPatternParser 在jmh基准测试下,有68倍吞吐量提升,降低30%40%空间分配率PathPatternParser 兼容 AntPathMatcher 语法,并支持更多类型的路径模式PathPatternParser **多段匹配的支持,仅允许是使用在表达式末尾
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @GetMapping("/a*/b?/{p1:[a-f]+}") public String hello (HttpServletRequest request, @PathVariable("p1") String path) log.info("路径变量p1: {}" , path); String uri = request.getRequestURI(); return uri; }
总结:
使用默认的路径匹配规则,是由 PathPatternParser 提供的
如果路径中间需要**,替换成ant风格路径1 2 3 4 spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy =ant_path_matcher
内容协商
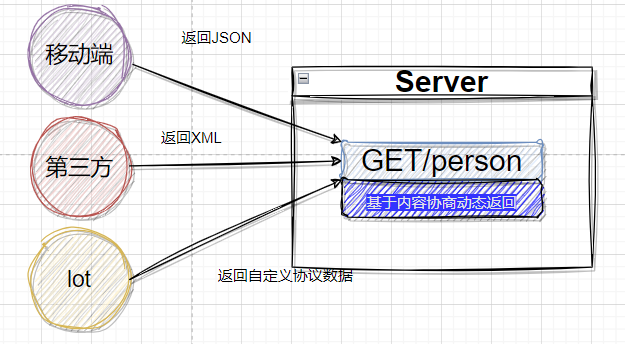
一套系统适配多端数据返回
多端内容适配 默认规则
SpringBoot多端内容适配
基于请求头 内容协商(默认开启)
客户端向服务端发送请求,携带HTTP标准的Accept请求头
Accept:application/json、text/xml、text/yaml
服务端根据客户端请求头期望的数据类型进行动态返回
基于请求参数 内容协商(需要自己开启)
发送请GET /project/spring-boot?format=json
匹配到@GetMapping("/project/spring-boot")
根据参数协商,优先返回json类型数据【需要开启参数匹配设置】
发送请求GET /project/spring-boot?format=xml,优先返回xml类型数据
效果演示
请求同一个接口,可以返回json和xml不同格式数据
引入支持写出xml内容的依赖(springboot默认情况下是不支持的)
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId > <artifactId > jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId > </dependency >
标注注解1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @JacksonXmlRootElement @Data public class Person private Long id; private String userName; private String email; private Integer age; }
开启基于请求参数的内容协商1 2 3 4 spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-parameter =true spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.parameter-name =type
效果http://127.0.0.1:8080/person?format=json1 2 3 4 5 6 { "id" : 1 , "userName" : "小明" , "email" : "1234.qq.com" , "age" : 12 }
http://127.0.0.1:8080/person?format=xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 <Person > <id > 1</id > <userName > 小明</userName > <email > 1234.qq.com</email > <age > 12</age > </Person >
配置协商规则与支持类型 自定义内容返回 增加yaml返回支持 导入依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId > <artifactId > jackson-dataformat-yaml</artifactId > </dependency >
把对象写出YAML
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static void main (String[] args) throws JsonProcessingException Person person = new Person(); person.setId(1L ); person.setUserName("张三" ); person.setEmail("aaa@qq.com" ); person.setAge(18 ); YAMLFactory factory = new YAMLFactory().disable(YAMLGenerator.Feature.WRITE_DOC_START_MARKER); ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(factory); String s = mapper.writeValueAsString(person); System.out.println(s); }
添加配置
1 2 spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.yaml =text/yaml
增加HttpMessageConverter组件,专门负责把对象写出为yaml格式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Bean public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer () return new WebMvcConfigurer() { @Override public void configureMessageConverters (List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) converters.add(new MyYamlHttpMessageConverter()); } }; }
思考:如何增加其他
配置媒体类型支持
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.yaml=text/yaml编写对应的HttpMessageConverter,要告诉boot整个支持的媒体类型
把自定义的HttpMessageConverter组件加入到底层
容器中国放一个WebMvcConfigurer组件,并配置底层的HttpMessageConverter
HttpMessageConverter的示例写法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class MyYamlHttpMessageConverter extends AbstractHttpMessageConverter <Object > private ObjectMapper objectMapper = null ; public MyYamlHttpMessageConverter () super (new MediaType("text" , "yaml" , Charset.forName("UTF-8" ))); YAMLFactory factory = new YAMLFactory() .disable(YAMLGenerator.Feature.WRITE_DOC_START_MARKER); this .objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(factory); } @Override protected boolean supports (Class<?> clazz) return true ; } @Override protected Object readInternal (Class<?> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException return null ; } @Override protected void writeInternal (Object methodReturnValue, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException try (OutputStream os = outputMessage.getBody()){ this .objectMapper.writeValue(os,methodReturnValue); } } }
内容协商原理-HttpMessageConverter
HttpMessageConverter 怎么工作?何时工作?定制 HttpMessageConverter 来实现多端内容协商
编写 WebMvcConfigurer 提供的 configureMessageConverters 方法,修改底层的 HttpMessageConverter
@ResponseBody 由 HttpMessageConverter 处理
标注了 @ResponseBody 的返回值将会由支持它的 HttpMessageConverter 写给浏览器
如果controller方法的返回值标注了 @ResponseBody 注解
请求先来到 DispatcherServlet 的 doDispatch() 方法进行处理
找到一个 HandlerAdapter 适配器,利用适配器执行目标方法
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 来执行,调用 invokeHandlerMethod() 方法来执行目标方法目标方法执行之前,准备号两个东西
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver :参数解析器,确定目标方法每个参数值HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler :返回值处理器,确定目标方法的返回值该怎么处理
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 里面的invokeAndHandle()真正执行目标方法目标方法执行完成,会返回返回值对象
找到一个合适的返回值处理器HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler
最终找到 RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 能处理标注了@ResponseBody注解的方法
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 调用 writeWithMessageConverters()方法,利用HttpMessageConverter把返回值写出去
上面解释:@ResponseBody 由 HttpMessageConverter 处理
HttpMessageConverter 会先进行内容协商
遍历所有的 HttpMessageConverter 看谁支持这种内容类型的数据
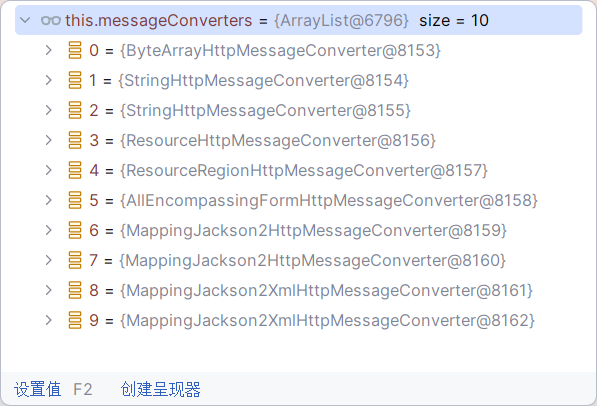
默认 HttpMessageConverter 有以下(其中最后两个xml的是新家的依赖,非默认):
最终因为要 json 所以 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 支持写出json
jackson用ObjectMapper 把对象写出去
WebMvcAutoConfiguration 提供几种默认 HttpMessageConverter
在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中有一个静态配置类 EnableWebMvcConfiguration 继承了 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration 又继承了WebMvcConfigurationSupport
WebMvcConfigurationSupport 通过 WebMvcConfigurationSupport() 方法添加了默认的 HttpMessageConverter
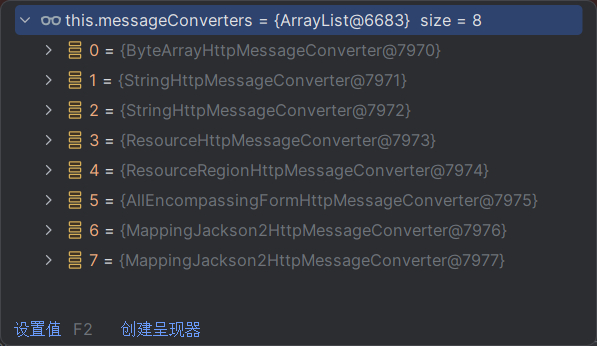
ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter :支持字节数据读写StringHttpMessageConverter :支持字符串读写ResourceHttpMessageConverter :支持资源读写ResourceRegionHttpMessageConverter :支持分区资源读写AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter :支持表单xml/json读写MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter :支持请求响应体Json读写
默认8个:
系统提供默认的HttpMessageConverter功能有限,见用于json或者普通返回数据,额外增加新的内容协商功能,需要增加新的HttpMessageConverter
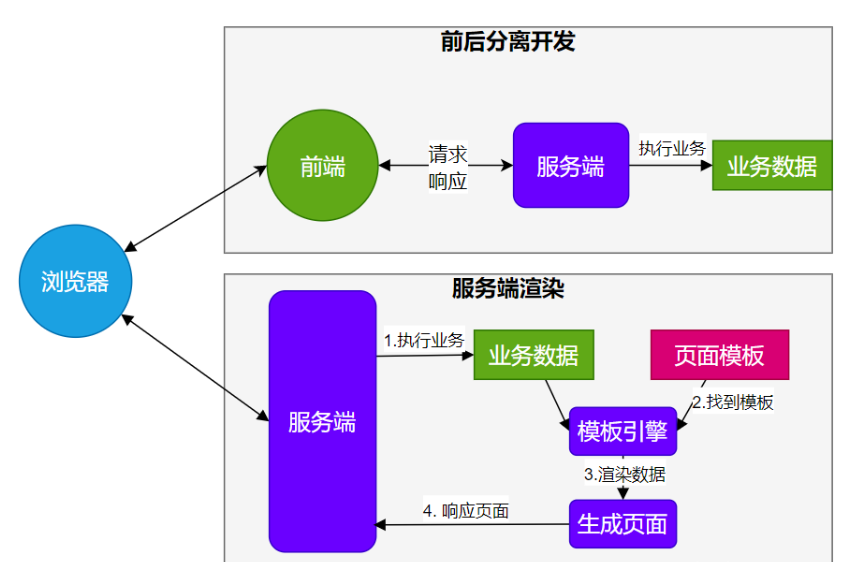
模板引擎
由于SpringBoot使用了嵌入式Servlet容器,所以JSP默认是不能使用的。
如果需要服务端页面渲染,优先考虑使用模板引擎。
模板引擎页面默认是放在src/main/resources/templates
FreeMarker
Groovy
Thymeleaf
MustacheThymeleaf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <!DOCTYPE html > <html xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head > <title > Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</title > <meta http-equiv ="Content-Type" content ="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> <link rel ="stylesheet" type ="text/css" media ="all" th:href ="@{/css/gtvg.css}" /> </head > <body > <p th:text ="#{home.welcome}" > Welcome to our grocery store!</p > </body </html >
Thymeleaf整合 添加依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId > </dependency >
自动配置原理
开启了org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration自动配置
属性绑定在ThymeleafProperties中,对应配置项spring.thymeleaf内容
所有的模板页面默认在classpath:/templates/
默认效果
所有模板页面在classpath:/templates/下面找
找后缀名为.html的页面基础语法
核心用法 th:xxx:动态渲染指定的html标签属性,或者th指令(遍历、判断等)
th:text:标签内文本值渲染
th:utext:不会转义,显示为html原本的样子。
th:属性:标签指定属性渲染th:attr:标签任意属性渲染th:if th:each ... :其他th指令例如1 2 3 4 <p th:text ="${content}" > 原内容</p > <a th:href ="${url}" > 登录</a > <img src ="../../images/gtvglogo.png" th:attr ="src=@{/images/gtvglogo.png},title=#{logo},alt=#{logo}" />
表达式:用来动态入取值
${}:变量取值;使用model共享给页面的值都直接使用${}@{}:url路径;#{}:国际化消息~{}:片段引用*{}:变量选择:需要配合th:object绑定对象
系统工具&内置对象:详细文档
param:请求参数对象session:session对象application:application对象#execInfo:模板执行信息#uris:uri/url工具#conversions:类型转换工具#dates:日期工具,是java.util.Date对象的工具类#calendars:类似#dates,只不过是java.util.Calender对象的工具类#temporals:JDK8+ java.timeAPI工具类#numbers:数字操作工具类#strings:字符串操作#objects:对象操作#bools:bool操作#arrays:array工具#lists:list工具#sets:set工具#maps:map工具#aggregates:集合聚合工具(sum、avg)#ids:id生成工具语法示例
表达式:
变量取值:${...}
url取值:@{...}
国际化消息:#{...}
变量选择:*{...}
片段引用:~{...}
常见:
文本操作:
拼串:+
文本替换:|The name is ${name}
布尔操作:
比较运算:
比较:> < <= >= (gt lt ge le)
等值运算:== != (eq ne)
条件运算:
if-then:(if)?(then)
if-then-else:(if)?(then):(else)
default:(value)?:(defauleValue)
特殊语法:
所有以上都可以嵌套组合:
1 'User is of type ' + (${user.isAdmin()} ? 'Administrator' : (${user.type} ?: 'Unknown'))
属性设置
th:href="@{/product/list}"th:attr="class=${active}"th:attr="src=@{/images/gtvglogo.png},title=${logo},alt=#{logo}"th:checked="${user.active}"
1 2 3 4 <p th:text ="${content}" > 原内容</p > <a th:href ="${url}" > 登录</a > <img src ="../../images/gtvglogo.png" th:attr ="src=@{/images/gtvglogo.png},title=#{logo},alt=#{logo}" />
遍历
语法:th:each="元素名,迭代状态 : ${集合}"
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <tr th:each ="prod : ${prods}" > <td th:text ="${prod.name}" > Onions</td > <td th:text ="${prod.price}" > 2.41</td > <td th:text ="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}" > yes</td > </tr > <tr th:each ="prod,iterStat : ${prods}" th:class ="${iterStat.odd}? 'odd'" > <td th:text ="${prod.name}" > Onions</td > <td th:text ="${prod.price}" > 2.41</td > <td th:text ="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}" > yes</td > </tr >
iterStat 有以下属性:
index:当前遍历元素的索引,从0开始count:当前遍历元素的索引,从1开始size:需要遍历元素的总数量current:当前正在遍历的元素对象even/odd:是否偶数/奇数行first:是否第一个元素last:是否最后一个元素
判断 th:if 1 2 3 4 5 <a href ="comments.html" th:href ="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}" th:if ="${not #lists.isEmpty(prod.comments)}" > view</a >
th:switch 1 2 3 4 5 <div th:switch ="${user.role}" > <p th:case ="'admin'" > User is an administrator</p > <p th:case ="#{roles.manager}" > User is a manager</p > <p th:case ="*" > User is some other thing</p > </div >
属性优先级
片段
遍历
判断1 2 3 <ul > <li th:each ="item : ${items}" th:text ="${item.description}" > Item description here...</li > </ul >
Order
Feature
Attributes
1
片段包含
th:insert th:replace
2
遍历
th:each
3
判断
th:if th:unless th:switch th:case
4
定义本地变量
th:object th:with
5
通用方式属性修改
th:attr th:attrprepend th:attrappend
6
指定属性修改
th:value th:href th:src …
7
文本值
th:text th:utext
8
片段指定
th:fragment
9
片段移除
th:remove
行内写法 [[...]] or [(...)]
1 <p > Hello, [[${session.user.name}]]!</p >
变量选择 1 2 3 4 5 <div th:object ="${session.user}" > <p > Name: <span th:text ="*{firstName}" > Sebastian</span > .</p > <p > Surname: <span th:text ="*{lastName}" > Pepper</span > .</p > <p > Nationality: <span th:text ="*{nationality}" > Saturn</span > .</p > </div >
等同于
1 2 3 4 5 <div > <p > Name: <span th:text ="${session.user.firstName}" > Sebastian</span > .</p > <p > Surname: <span th:text ="${session.user.lastName}" > Pepper</span > .</p > <p > Nationality: <span th:text ="${session.user.nationality}" > Saturn</span > .</p > </div
模板布局
定义模板: th:fragment
引用模板:~{templatename::selector}
插入模板:th:insert、th:replace
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <footer th:fragment ="copy" > © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</footer > <body > <div th:insert ="~{footer :: copy}" > </div > <div th:replace ="~{footer :: copy}" > </div > </body > <body > 结果: <body > <div > <footer > © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</footer > </div > <footer > © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</footer > </body > </body >
国际化 国际化的自动配置参照MessageSourceAutoConfiguration
实现步骤 :
Spring Boot 在类路径根下查找messages资源绑定文件。文件名为:messages.properties
多语言可以定义多个消息文件,命名为messages_区域代码.properties。如:
messages.properties:默认messages_zh_CN.properties:中文环境messages_en_US.properties:英语环境
在程序中 可以自动注入 MessageSource组件,获取国际化的配置项值
在页面中 可以使用表达式 #{}获取国际化的配置项值1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Autowired //国际化取消息用的组件 MessageSource messageSource; @GetMapping("/haha") public String haha(HttpServletRequest request){ Locale locale = request.getLocale(); //利用代码的方式获取国际化配置文件中指定的配置项的值 String login = messageSource.getMessage("login", null, locale); return login; }
错误处理 默认机制
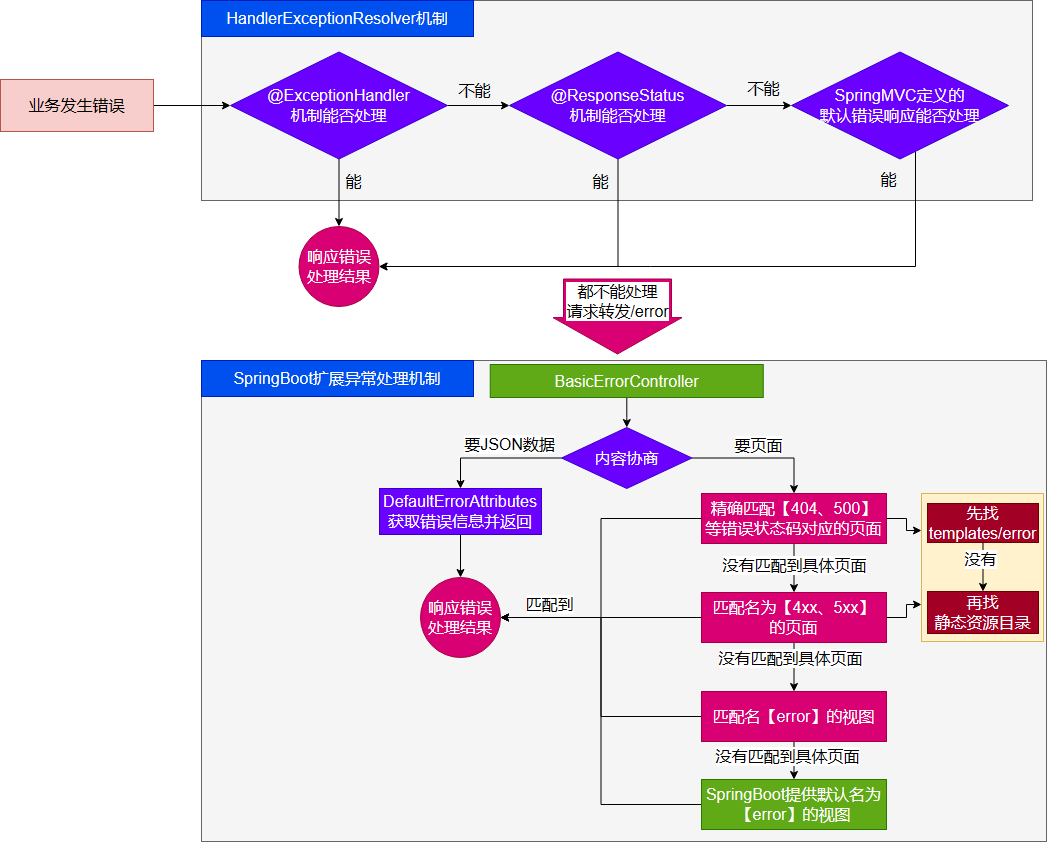
错误处理的自动偶配置都在ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration中,两大核心机制:
SpringBoot会自适应 处理错误,响应页面 或JSON数据
SpringMVC的错误处理机制依然保留,MC处理不了,才会交给boot进行处理
发生错误以后,转发给/error路径,SpringBoot在底层写好了一个BasicErrorController的组件,专门处理这个请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) public ModelAndView errorHtml (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); Map<String, Object> model = Collections .unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML))); response.setStatus(status.value()); ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); return (modelAndView != null ) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error" , model); } @RequestMapping public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) { return new ResponseEntity<>(status); } Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL)); return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status); }
错误页面是怎么解析到的1 2 3 4 ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); return (modelAndView != null ) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error" , model);
容器中专门有一个错误视图解析器
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Bean @ConditionalOnBean(DispatcherServlet.class) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(ErrorViewResolver.class) DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver () { return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this .applicationContext, this .resources); }
SpringBoot解析自定义错误页面的默认规则
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 @Override public ModelAndView resolveErrorView (HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model); if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) { modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model); } return modelAndView; } private ModelAndView resolve (String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName; TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this .templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName, this .applicationContext); if (provider != null ) { return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model); } return resolveResource(errorViewName, model); } private ModelAndView resolveResource (String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) for (String location : this .resources.getStaticLocations()) { try { Resource resource = this .applicationContext.getResource(location); resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html" ); if (resource.exists()) { return new ModelAndView(new HtmlResourceView(resource), model); } } catch (Exception ex) { } } return null ; }
容器中有一个默认的名字为error的view;提供了默认的白页功能
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Bean(name = "error") @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "error") public View defaultErrorView () return this .defaultErrorView; }
封装了JSON格式的错误信息
1 2 3 4 5 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes () return new DefaultErrorAttributes(); }
规则
解析一个错误页
如果发生了500、404、503、403这些错误
如果有模板引擎,默认在classpath:/templates/error/精确码.html
如果没有模板引擎,或者没有找到,就去静态资源文件夹下找,精确码.html
如果匹配不到精确码.html这些精确的错误页,就去找5xx.html 4xx.html模糊匹配
如果有模板引擎默认在classpath:/templates/error/5xx.html
如果没有模板引擎或者没找到,在静态资源文件夹下找5xx.html
如果模板引擎路径templates有error.html页面就直接渲染
自定义错误响应 自定义json响应
使用@ControllerAdvice或@ControllerAdvice 配合@ExceptionHandler进行统一异常处理
自定义页面响应
根据boot的错误页面规则,自定义页面模板
最佳实战
前后端分离
后端发生的所有错误,@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler进行统一异常处理
服务端页面渲染
不可预知的一些,HTTP码表示的服务器或客户端错误
给classpath:/templates/error/下面,放常用精确的错误码页面。500.html 404.html
给classpath:/templates/error/下面,放模糊匹配的错误码页面。5xx.html 4xx.html
发生业务错误
核心业务 ,每一种错误,都应该代码控制,跳转到自己定制的错误页通用业务 ,classpath:/templates/error.html页面,显示错误信息1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes (WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)); if (!options.isIncluded(Include.EXCEPTION)) { errorAttributes.remove("exception" ); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)) { errorAttributes.remove("trace" ); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.MESSAGE) && errorAttributes.get("message" ) != null ) { errorAttributes.remove("message" ); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.BINDING_ERRORS)) { errorAttributes.remove("errors" ); } return errorAttributes; }
嵌入式容器
Servlet容器 :管理、运行Servlet组件(Servlet、Filter、listener)的环境,一般指服务器
自动配置原理
SpringBoot默认嵌入Tomcat作为Servlet容器
自动配置类是ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration
自动配置类开始分析功能,xxxxAutoConfiguration
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @AutoConfiguration(after = SslAutoConfiguration.class) @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE) @ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class) @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) @EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class) @Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class, ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class, ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class, ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class }) public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration自动配置了嵌入式容器场景绑定了ServerProperties配置类,所有和服务器有关的配置server
自定义 最佳实战 全面接管SpringMVC WebMvcAutoConfiguration到底自动配置了哪些规则 最佳实战 三种方式
方式
用法
效果
全自动
直接编写控制器逻辑
全部使用自动配置默认效果
手自一体 @Configuration +WebMvcConfigurer+ 不要标注 @EnableWebMvc保留自动配置效果 手动设置部分功能
全手动 @Configuration +WebMvcConfigurer标注 @EnableWebMvc禁用自动配置效果
总结:@Configuration实现WebMvcConfigurer接口,但是不要标注@EnableWebMvc注解,实现手自一体的效果。
两种模式
前后端分离模式:@RestController1响应JSON数据
前后不分离模式:@Controller+Thymeleaf模板引擎
Web新特性 Problemdetails
RFC 7807 :RFC 7807: Problem Details for HTTP APIs (rfc-editor.org)
原理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc.problemdetails", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true") static class ProblemDetailsErrorHandlingConfiguration @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(ResponseEntityExceptionHandler.class) @Order(0) ProblemDetailsExceptionHandler problemDetailsExceptionHandler () { return new ProblemDetailsExceptionHandler(); } }
ProblemDetailsExceptionHandler是一个@ControllerAdvice集中处理系统异常处理以下异常,如果系统出现以下异常,会被SpringBoot支持以RFC 7807规范方式反水错误数据1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @ExceptionHandler({ HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class,//请求方式不支持 HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException.class, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException.class, MissingPathVariableException.class, MissingServletRequestParameterException.class, MissingServletRequestPartException.class, ServletRequestBindingException.class, MethodArgumentNotValidException.class, HandlerMethodValidationException.class, NoHandlerFoundException.class, NoResourceFoundException.class, AsyncRequestTimeoutException.class, ErrorResponseException.class, MaxUploadSizeExceededException.class, ConversionNotSupportedException.class, TypeMismatchException.class, HttpMessageNotReadableException.class, HttpMessageNotWritableException.class, MethodValidationException.class, BindException.class }
默认响应错误的json,状态码405
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 { "timestamp" : "2023-04-18T11:13:05.515+00:00" , "status" : 405 , "error" : "Method Not Allowed" , "trace" : "org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException: Request method 'POST' is not supported\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.handleNoMatch(RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.java:265)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.lookupHandlerMethod(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java:441)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.getHandlerInternal(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java:382)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.getHandlerInternal(RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.java:126)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.getHandlerInternal(RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.java:68)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping.getHandler(AbstractHandlerMapping.java:505)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.getHandler(DispatcherServlet.java:1275)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doDispatch(DispatcherServlet.java:1057)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doService(DispatcherServlet.java:974)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.processRequest(FrameworkServlet.java:1011)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.doPost(FrameworkServlet.java:914)\r\n\tat jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:563)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.service(FrameworkServlet.java:885)\r\n\tat jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:631)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:205)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsFilter.doFilter(WsFilter.java:53)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:174)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.RequestContextFilter.doFilterInternal(RequestContextFilter.java:100)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:116)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:174)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.FormContentFilter.doFilterInternal(FormContentFilter.java:93)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:116)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:174)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter.doFilterInternal(CharacterEncodingFilter.java:201)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:116)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:174)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve.invoke(StandardWrapperValve.java:166)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve.invoke(StandardContextValve.java:90)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.authenticator.AuthenticatorBase.invoke(AuthenticatorBase.java:493)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.invoke(StandardHostValve.java:115)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve.invoke(ErrorReportValve.java:93)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve.invoke(StandardEngineValve.java:74)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.service(CoyoteAdapter.java:341)\r\n\tat org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Processor.service(Http11Processor.java:390)\r\n\tat org.apache.coyote.AbstractProcessorLight.process(AbstractProcessorLight.java:63)\r\n\tat org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$ConnectionHandler.process(AbstractProtocol.java:894)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint$SocketProcessor.doRun(NioEndpoint.java:1741)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SocketProcessorBase.run(SocketProcessorBase.java:52)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1191)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:659)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread$WrappingRunnable.run(TaskThread.java:61)\r\n\tat java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:833)\r\n" , "message" : "Method 'POST' is not supported." , "path" : "/list" }
开启ProblemDetails返回,使用新的MediaTypeContent-type: application/problem+json+额外扩展返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 { "type" : "about:blank" , "title" : "Method Not Allowed" , "status" : 405 , "detail" : "Method 'POST' is not supported." , "instance" : "/list" }
函数式web
SpringMVC 5.2以后允许我们使用函数式的方式,定义web的请求处理流程。
@Controller+@RequestMapping:耦合式(路由、业务耦合)函数式web:分离式(路由、业务分离)
场景 场景:User RESTful - CRUD
GET /user/1 获取1号用户
GET /users 获取所有用户
POST /user 请求体 携带JSON,新增一个用户
PUT /user/1 请求体 携带JSON,修改1号用户
DELETE /user/1 删除 1号用户
核心类
RouterFunction :定义路由信息。发什么请求,谁来处理 RequestPredicate :定义请求规则:请求谓语。请求方式(GET、POST)、请求参数 ServerRequest :封装请求完整数据 ServerResponse : 封装响应完整数据
函数式Web:
示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.http.MediaType;import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.RequestPredicate;import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.RouterFunction;import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.ServerResponse;import static org.springframework.web.servlet.function.RequestPredicates.accept;import static org.springframework.web.servlet.function.RouterFunctions.route;@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) public class MyRoutingConfiguration private static final RequestPredicate ACCEPT_JSON = accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON); @Bean public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> routerFunction (MyUserHandler userHandler) return route() .GET("/{user}" , ACCEPT_JSON, userHandler::getUser) .GET("/{user}/customers" , ACCEPT_JSON, userHandler::getUserCustomers) .DELETE("/{user}" , ACCEPT_JSON, userHandler::deleteUser) .build(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.ServerRequest;import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.ServerResponse;@Component public class MyUserHandler public ServerResponse getUser (ServerRequest request) ... return ServerResponse.ok().build(); } public ServerResponse getUserCustomers (ServerRequest request) ... return ServerResponse.ok().build(); } public ServerResponse deleteUser (ServerRequest request) ... return ServerResponse.ok().build(); } }